
10 月 . 22, 2024 05:19 Back to list
Comprehensive Guide to Deep Groove Ball Bearings Specifications and Applications
Understanding Deep Groove Ball Bearings A Comprehensive Overview
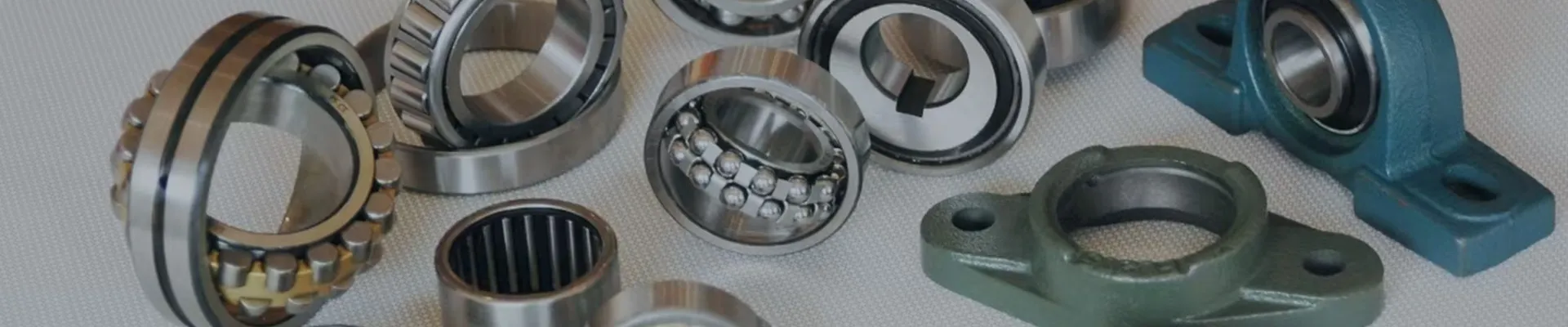
Deep groove ball bearings are among the most widely used types of rolling bearings. Their simplicity and versatility have made them a crucial component in various machines and applications across multiple industries. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of deep groove ball bearings, exploring their design, function, applications, and advantages.
Design Features
Deep groove ball bearings consist of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage that separates the balls and retains them in position. The design of these bearings is noteworthy for its deep raceway grooves, which allow for the accommodation of both radial and axial loads. The deep grooves facilitate a higher contact angle between the balls and the races, resulting in enhanced load-carrying capacity.
These bearings are typically made of high-quality steel, although ceramic and polymer materials may also be used for specific applications. The surfaces are meticulously ground and polished to ensure smooth operation and minimize friction.
Function and Operation
The primary function of deep groove ball bearings is to reduce friction between the moving parts of a machine, allowing for smoother operation. They achieve this by providing a low-friction surface for rotation, which results in less wear and tear over time. The ability to manage both radial and axial loads makes them ideal for various mechanical setups.
When a rotating shaft is subjected to radial loads, the balls inside the bearing roll along the grooves, distributing the load evenly. If axial forces are introduced, the design of the raceways allows the bearings to accommodate these forces effectively. This versatility makes deep groove ball bearings suitable for applications where changing load conditions are common.
Common Applications
Deep groove ball bearings are utilized in a myriad of applications across different industries. Some common uses include
deep groove ball bearing catalogue pdf
2. Industrial Machinery These bearings support rotating shafts in manufacturing equipment, pumps, and conveyors, optimizing productivity and minimizing downtime.
3. Electrical Appliances From washing machines to power tools, deep groove ball bearings facilitate the operation of motors and other moving parts.
4. Aerospace Their ability to handle extreme conditions makes them ideal for use in aircraft systems and components.
Advantages
The advantages of deep groove ball bearings contribute to their widespread adoption
1. Cost-Effectiveness They are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and maintain, providing a robust solution for many applications.
2. High Load Capacity Their design allows them to handle substantial loads while maintaining operational efficiency.
3. Versatility Capable of accommodating both radial and axial loads, deep groove ball bearings can be used in various settings, from light-duty to heavy industrial applications.
4. Low Maintenance Once installed, these bearings require minimal upkeep, making them ideal for applications where maintenance accessibility is challenging.
Conclusion
Deep groove ball bearings play a vital role in modern machinery and equipment. Their unique design, combined with the ability to manage both radial and axial loads, makes them a versatile choice for countless applications. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for efficient and reliable bearings will only grow, ensuring that deep groove ball bearings remain a foundational element of engineering and manufacturing processes around the world. Understanding their features and applications can aid engineers and designers in selecting the right bearings to meet their operational needs effectively.
Latest news
-
Unlocking Efficiency with Spherical Roller Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Thrust Ball Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power of Thrust Roller Bearings: Engineered for Excellence
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power of Deep Groove Ball Bearings for Your Application Needs!
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power and Performance of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
High-Quality Ball Bearing Manufacturing Machines
NewsOct.29,2024
