
11 月 . 02, 2024 13:44 Back to list
deep groove ball bearing catalogue pdf
Understanding Deep Groove Ball Bearings A Comprehensive Overview
Deep groove ball bearings are among the most widely used types of bearings in various industrial applications. Their design allows them to support both radial and axial loads, making them versatile components in machinery and equipment. This article aims to provide insight into the characteristics, applications, and benefits of deep groove ball bearings, referencing information typically found in a detailed catalogue.
Design and Structure
A deep groove ball bearing comprises an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage that holds the balls in place. The deep groove design refers to the shape of the raceway, which has a deeper profile compared to standard ball bearings. This feature enhances the bearing's ability to accommodate higher radial loads and axial loads in both directions, allowing for a broader range of applications.
Material and Construction
Deep groove ball bearings are generally constructed from high-quality steel, though variations made from ceramic or hybrid materials are also available. The choice of material greatly influences the bearing's performance, durability, and resistance to corrosion. The inner and outer rings are typically hardened for added strength, and many bearings also feature shields or seals to protect against contaminants, thereby extending their service life.
deep groove ball bearing catalogue pdf
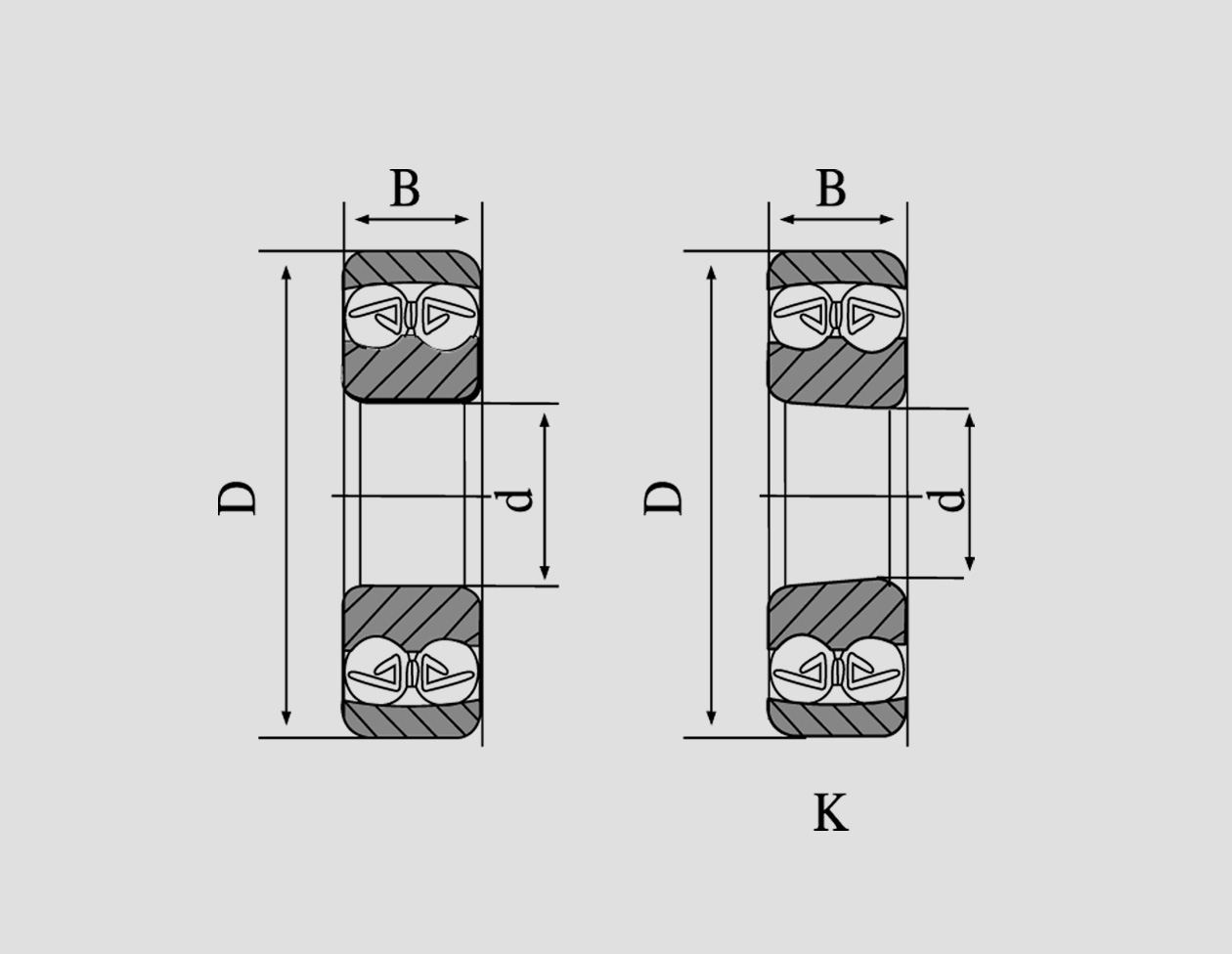
Applications
These bearings are utilized in various sectors, such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and consumer electronics. In automotive applications, for instance, they are found in motors, gearboxes, and wheel hubs. Their low friction and high durability make them ideal for machinery subjected to continuous operation. In the consumer electronics realm, they play a crucial role in devices like washing machines, air conditioners, and computer hard drives.
Benefits of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
One of the main advantages of deep groove ball bearings is their ability to operate at high speeds, making them suitable for equipment that demands quick rotations. Their design also allows for low friction, which translates to reduced energy consumption and improved efficiency in various applications. Furthermore, they can handle misalignment to some extent, offering operational reliability even in less-than-ideal conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, deep groove ball bearings are essential components in a wide array of mechanical systems. Their robust design, versatility, and ability to accommodate both radial and axial loads make them invaluable in many industries. Understanding the specifications and features outlined in a comprehensive catalogue can aid engineers and manufacturers in selecting the right bearings for their applications, ultimately enhancing performance and longevity. As technology evolves, we can expect continual improvements in bearing design and materials, further solidifying the role of deep groove ball bearings in modern engineering solutions.
Latest news
-
Unlocking Efficiency with Spherical Roller Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Thrust Ball Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power of Thrust Roller Bearings: Engineered for Excellence
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power of Deep Groove Ball Bearings for Your Application Needs!
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power and Performance of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
High-Quality Ball Bearing Manufacturing Machines
NewsOct.29,2024
