
8 月 . 19, 2024 22:16 Back to list
High-Performance 6000 Series Sealed Ball Bearings for Various Applications
Understanding the 6000 2RS Ball Bearing A Comprehensive Guide
Ball bearings are essential components in various mechanical systems, serving the crucial purpose of reducing friction between moving parts and facilitating smooth motion. Among the numerous types available in the market, the 6000 2RS ball bearing stands out due to its versatile applications, robust design, and high performance. This article will explore what defines the 6000 2RS ball bearing, its specifications, construction, advantages, and common applications.
Specifications and Design
The nomenclature 6000 refers to a specific series of ball bearings standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The 2RS suffix indicates that the bearing is equipped with two rubber seals, one on either side. These seals serve to protect the internal components from contaminants such as dirt, dust, and moisture, while also retaining lubrication within the bearing.
The typical dimensions of a 6000 series ball bearing include an inner diameter of 10 mm, an outer diameter of 26 mm, and a width of 8 mm. However, these dimensions may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer. The bearing usually contains deep groove raceways, allowing for both radial and axial loads, which contributes to its versatility.
Construction
The construction of the 6000 2RS ball bearing comprises key elements that ensure its efficiency and longevity. The most notable feature is its steel balls, which are responsible for facilitating movement and reducing friction. These steel balls are housed within an inner and outer raceway. The entire assembly is lubricated with a high-quality grease that not only provides a smooth operational experience but also enhances the bearing's resistance to wear and heat generation.
The rubber seals, or shields, are another vital aspect of the 6000 2RS design. They are manufactured from durable materials that can withstand significant wear over time. These seals keep contaminants out and retain the lubricant, thereby prolonging the bearing's lifespan. In many cases, the bearings are sealed and pre-lubricated at the factory, which helps to simplify installation and maintenance for end-users.
Advantages of 6000 2RS Ball Bearings
The 6000 2RS ball bearing boasts several advantages that make it a popular choice across various industries
ball bearing 6000 2rs
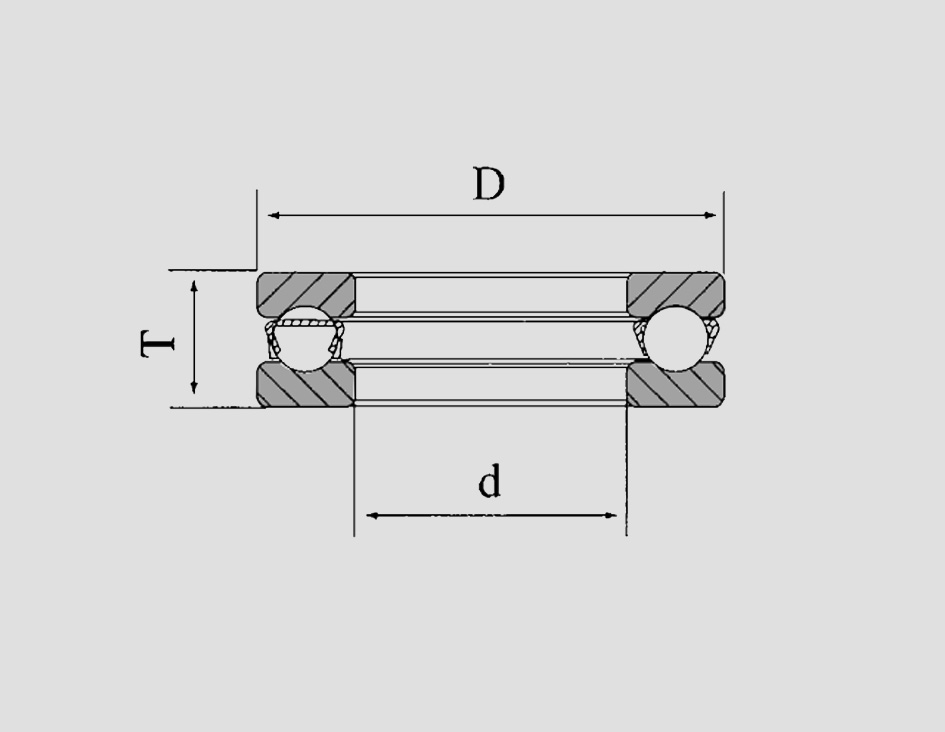
1. Versatility This bearing can be used in numerous applications, from electric motors and fans to bicycles and household appliances. Its ability to handle both radial and axial loads makes it adaptable to different mechanical setups.
2. Durability The sealed design minimizes exposure to contaminants, which significantly improves the bearing’s life expectancy. Additionally, high-quality materials are used in construction, providing resilience against wear and corrosion.
3. Low Maintenance The factory lubrication and sealing minimize the need for frequent maintenance, making it a cost-effective option for both manufacturers and consumers alike.
4. Smooth Operation The precision design and quality materials contribute to reduced friction, leading to quieter and smoother operation of machinery.
Common Applications
Given its robust performance and durability, the 6000 2RS ball bearing is utilized in various sectors, such as
- Automotive In applications like wheel hubs and electric motors. - Industrial Equipment Commonly found in conveyor systems, pumps, and actuators. - Consumer Electronics Used in fans, hard drives, and home appliances. - Bicycles Integrated into hubs and bottom brackets for optimal performance.
Conclusion
The 6000 2RS ball bearing is an excellent example of engineering efficiency and reliability. With its robust design, low-maintenance characteristics, and versatility, it serves as a cornerstone in many mechanical systems. Understanding its specifications and applications helps engineers and consumers alike make informed decisions when selecting the ideal bearing for their needs. Whether in an industrial setting or at home, the 6000 2RS ball bearing continues to play an integral role in facilitating smooth, efficient motion across a multitude of devices and machines.
Latest news
-
Unlocking Efficiency with Spherical Roller Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Thrust Ball Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power of Thrust Roller Bearings: Engineered for Excellence
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power of Deep Groove Ball Bearings for Your Application Needs!
NewsOct.29,2024
-
The Power and Performance of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
NewsOct.29,2024
-
High-Quality Ball Bearing Manufacturing Machines
NewsOct.29,2024
